The Australian Pesticides and Veterinary Medicines Authority (APVMA) is an independent statutory authority with responsibility for assessing and approving agricultural and veterinary chemical products prior to their sale and use in Australia. Metasystox R Systemic Insecticide can be safely used by workers when handled in accordance with the control measures indicated in this assessment.
In undertaking this task, the APVMA works in close cooperation with advisory agencies, including the Department of Health and Family Services (Therapeutic Goods Administration), Environment Australia (Risk Assessment and Policy Section), the National Occupational Health and Safety Commission (Worksafe Australia) and State departments of agriculture and environment.
The APVMA has a policy of encouraging openness and transparency in its activities and of seeking community involvement in decision making. Part of that process is the publication of public release summaries for all products containing new active ingredients and for all proposed extensions of use for existing products.
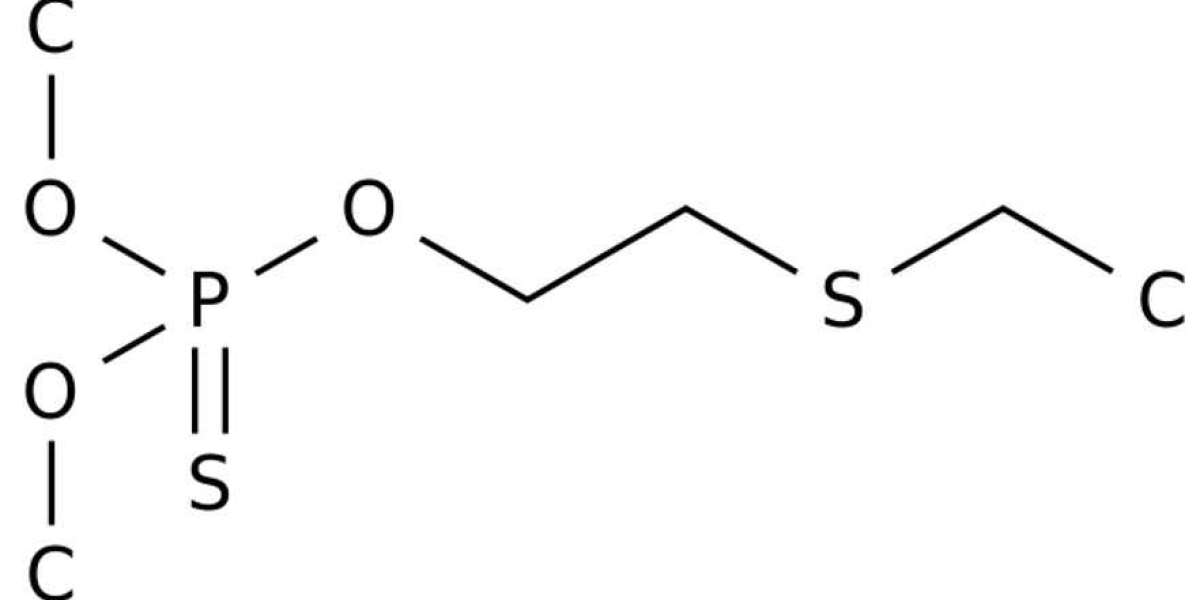
Oxydemeton-methyl is a slight eye irritant in rabbits, and is not a skin sensitiser in guinea pigs. The product, Metasystox R Systemic Insecticide containing 25% of oxydemeton-methyl, has moderate acute oral and dermal toxicity. The product is a slight skin, and a moderate eye irritant in rabbits and is likely to cause skin sensitisation.
Oxydemeton-methyl is rapidly and extensively absorbed orally and rapidly excreted, primarily as the unchanged compound, in urine. Significant tissue accumulation does not occur.
Oxydemeton-methyl is an organophosphorus compound. Adverse clinical signs associated with exposure to chemicals of this class relate to the rapid decline in brain and blood cholinesterases (enzymes which break down the nerve signal transmitter acetyl choline and related compounds). The result is accumulation of acetylcholine within the nervous system which leads to excessive nerve stimulation manifested as salivation, muscle tremors and depression. Organ or tissue damage was not noted in repeat dose studies with oxydemeton-methyl.
Female fertility rates are reduced in rats when they are given high doses of oxydemeton-methyl. In most studies, no adverse effects are reported on male reproduction, suggesting that the chemical may be acting primarily on female reproductive performance at high doses. However in one study, male rats showed reduced sperm motility. A consistent finding in males was microscopic change in the cells of the epididymides (vacuolation) which was seen after repeated exposure. Male fertility was not affected, however.
Results from Brussels sprouts, cabbage, cauliflower, cotton, and lupin residue trials conducted in Australia allowed the establishment of oxydemeton-methyl MRLs for brassica vegetable crops, head cabbages, and flowerhead brassica, cotton seed, cotton seed oil (crude), and lupins (dry). Overseas cotton data also supported the proposed cottonseed and oil MRLs. Animal commodity MRLs for eggs, edible offal (mammalian), meat (mammalian), milks, edible poultry offal, and poultry meat were also established along with cotton and lupin forage MRLs. When Metasystox R Systemic Insecticide is used to control aphids according to the proposed use patterns the recommended MRLs are not expected to be exceeded.
The residue definition is the sum of oxydemeton-methyl and demeton-S-methyl sulphone, expressed as oxydemeton-methyl. This differs from the Codex Alimentarius oxydemeton-methyl residue definition of sum of oxydemeton-methyl, demeton-S-methyl and demeton-S-methylsulphone, expressed as oxydemeton-methyl. The Australian residue definition is based on Good Agricultural Practice in Australia and the present analytical technology, which measures the oxydemeton-methyl as its sulphone derivative. Residue data indicated that sulphone metabolite occurs in minor quantities.