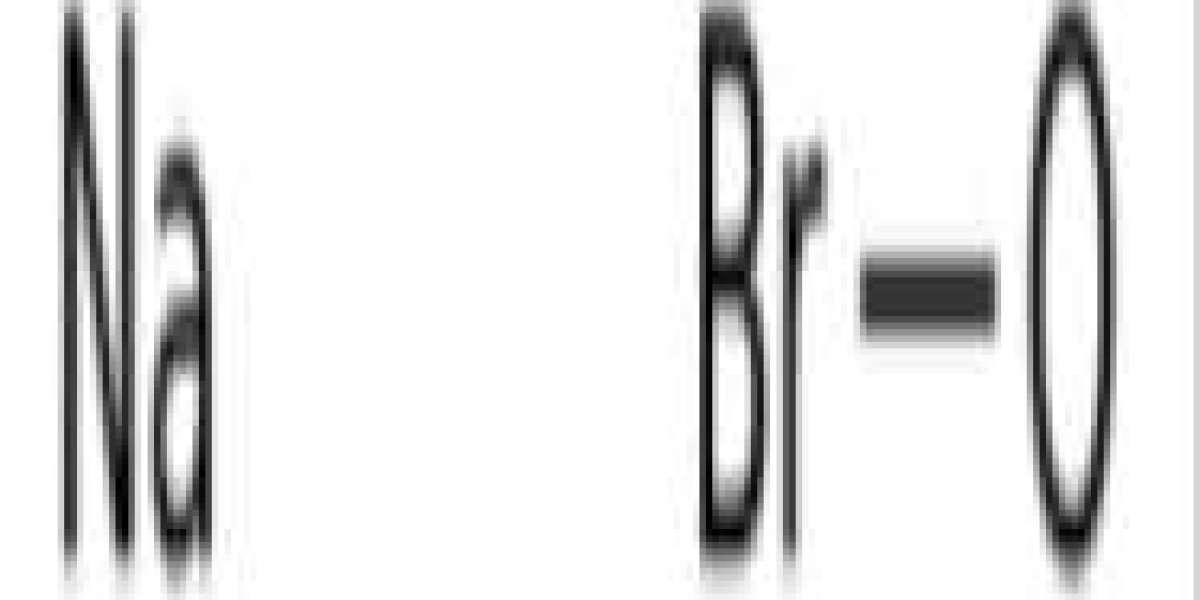Dietary bromide, which occurs naturally in the blood, is used by eosinophils (granulocyte-like white blood cells) specialized in dealing with multicellular parasites. These cells react bromide with peroxide to generate hypobromite through the action of eosinophil peroxidase, a haloperoxidase that preferentially uses bromide rather than Chloride for this purpose. [3]
Simple bromide salts, such as sodium bromide, are also sometimes used as mild antiseptics in hot tubs and spas, using the action of added oxidizing agents such as hydrogen peroxide to generate hypobromite in situ, the way it works Effect of peroxidase on bromide with eosinophils.
Hypobromite has been proposed to be a reactive intermediate in the Hofmann rearrangement.
These reactions of bromine are similar to the reactions of chlorine to form hypochlorite and chlorate. The corresponding chlorine reaction 1 (formation of ClO−) is fast at 20 °C and reaction 2 (formation of ClO−
3) Slow at 20 °C, fast at 70 °C.
What is hypobromite used for?
Hypobromite is a bromine compound similar to common bleach and hypochlorite found in immune cells. In many ways, hypobromite functions in the same way as hypochlorite, and is also used as a fungicide and antiparasitic in industrial applications and in the immune system.
Is hypobromite an acid?
Hypobromous acid is an unstable weak acid with the chemical formula HBrO, in which the bromine atom is in the +1 oxidation state. It is also known as "bromohydrin" or "hydroxybromide." It exists only in solution and has very similar chemical and physical properties to hypochlorous acid HClO.