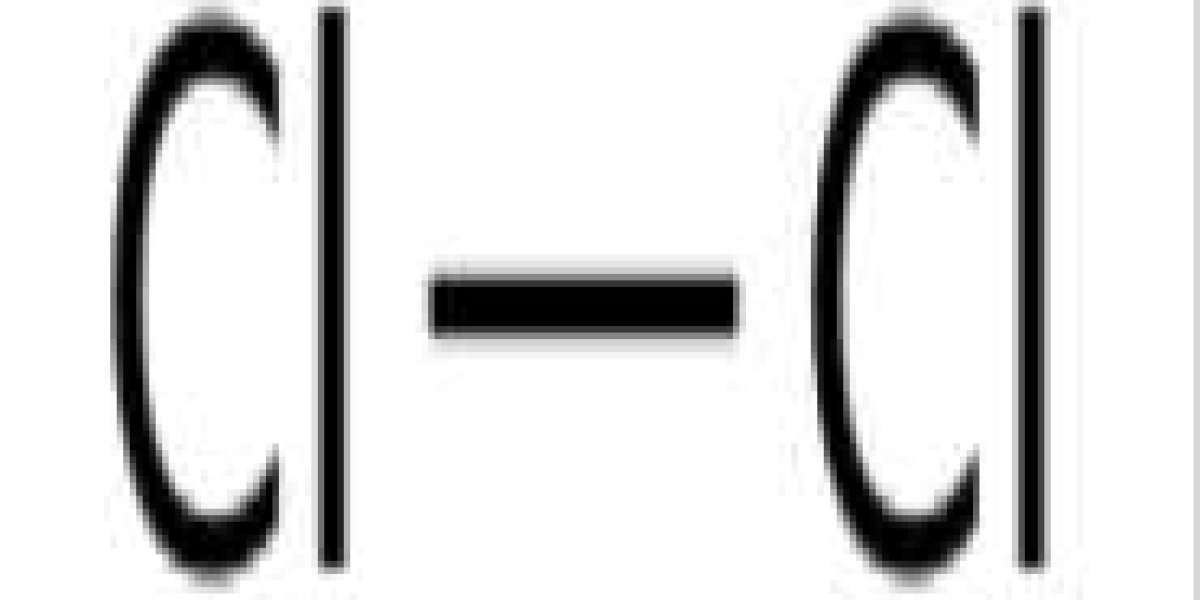Chlorine is a chemical element with the symbol Cl and atomic number 17. It is the second lightest element among halogens, between fluorine and bromine in the periodic table, and its properties are mostly between the two. Chlorine is a yellow-green gas at room temperature. It is an extremely reactive element and a strong oxidizing agent: among the elements it has the highest electron affinity and the third highest electronegativity on the modified Pauling scale, after oxygen and fluorine.
Chlorine played an important role in experiments performed by medieval alchemists, which often involved the heating of chloride salts such as ammonium chloride (sal ammoniac) and sodium chloride (common salt), producing various chlorine-containing chemicals such as hydrogen chloride , mercury(II) chloride (a corrosive sublimate) and hydrochloric acid (in the form of aqua regia). However, the properties of free chlorine as a separate substance were not recognized until around 1630 by Jan Baptist van Helmont. Carl Wilhelm Scheele wrote a description of chlorine gas in 1774, positing it as an oxide of a new element. In 1809, chemists suggested that the gas might be a pure element, which was confirmed by Sir Humphrey Davy in 1810 and named after the ancient Greek χλωρός (khlōrós, "pale green") for its color .
Because of its extreme reactivity, all chlorine in the Earth's crust exists as ionic chloride, which includes table salt. It is the second most abundant halogen (after fluorine) and the twenty-first most abundant chemical element in the Earth's crust. However, these crustal deposits are dwarfed by the enormous reserves of chloride in seawater.